SMILE- It costs nothing !!!
Alveolar Bone: Key to Oral Health
Discover the vital role of alveolar bone in oral health. Learn about its structure, function, and how it supports teeth. Enhance your knowledge of this essential component for maintaining a healthy smile!
3/3/20252 min read
Alveolar Bone
What Is the Alveolar Bone?
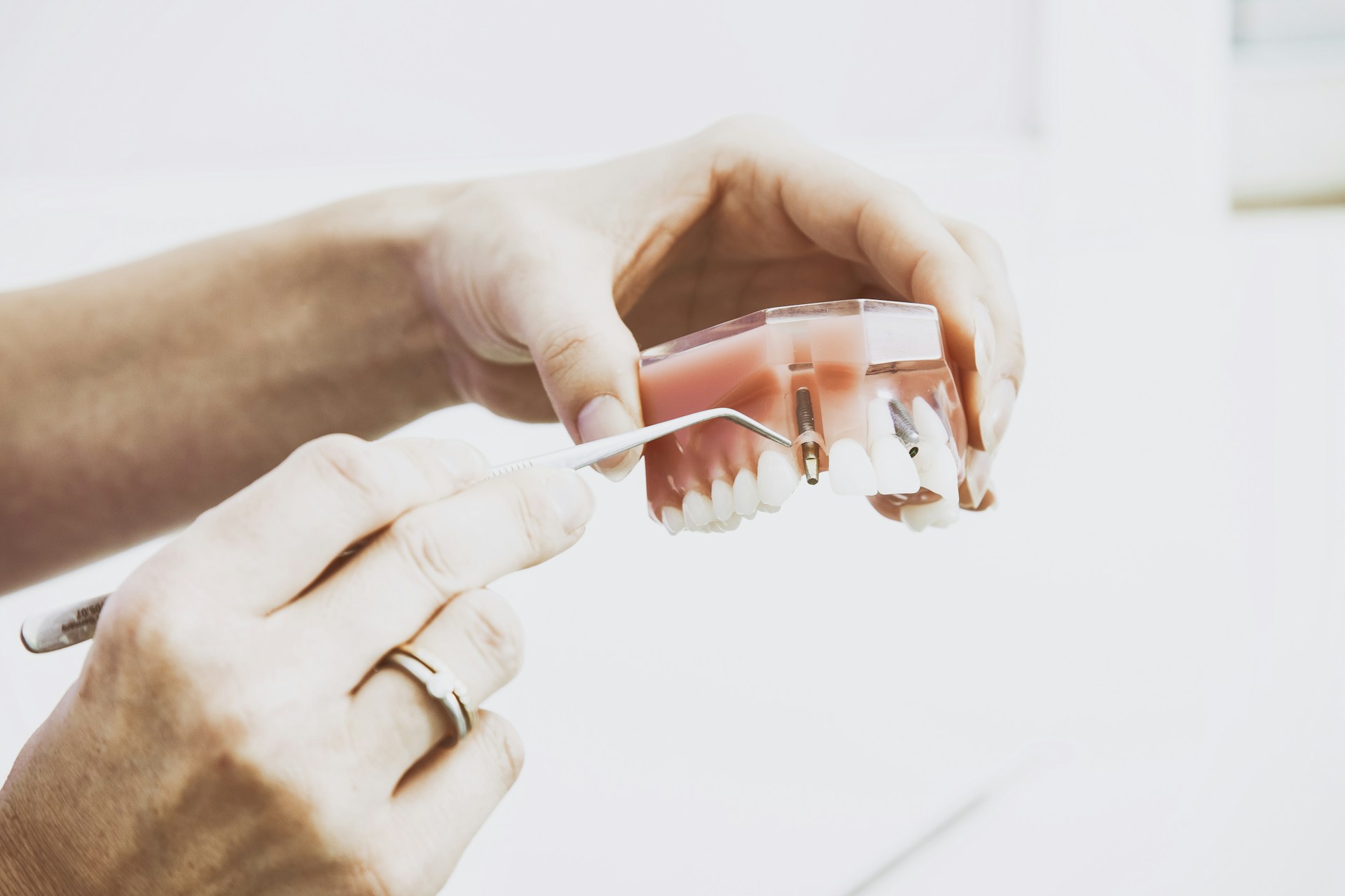
The alveolar bone is a crucial component of the human jaw that supports and holds teeth in place (Schroeder, 1986).
It forms the sockets, known as dental alveoli, where the tooth roots are anchored (Ten Cate, 2012).
This specialized bone structure is continuously remodeled throughout life, responding to mechanical stresses like chewing and tooth loss.
Structure of the Alveolar Bone
The alveolar process is the part of the jawbone that contains the dental alveoli (Lindhe, Lang, & Karring, 2008). It is divided into two sections based on the jaw:
Alveolar Process of Maxilla Bone – The upper jaw's portion that holds the upper teeth.
Mandibular Alveolar Process – The lower jaw's portion that supports the lower teeth.
Both these structures form the alveolar ridge in the mouth, providing the necessary support for functional teeth alignment and stability.
Functions of the Alveolar Bone
The alveolar bone serves several essential roles, including:
Tooth Support: It holds the teeth securely within the dental alveoli.
Shock Absorption: During biting and chewing, it distributes forces efficiently.
Bone Remodeling: The bone adapts to changes due to tooth movement or loss.
Development and Remodeling of Alveolar Bone
The alveolar process develops alongside teeth.
Once a tooth erupts, the dental alveoli form around it.
However, if teeth are lost, the alveolar ridge in the mouth begins to resorb, leading to bone loss (Misch, 2007). This process underscores the importance of maintaining healthy teeth to preserve the integrity of the alveolar process of maxilla bone and the mandibular alveolar process.
Common Conditions Affecting the Alveolar Bone
Periodontal Disease: Infections and inflammation can lead to bone loss.
Tooth Loss: Without stimulation from teeth, the alveolar process undergoes resorption.
Trauma and Fractures: Accidents can damage the alveolar ridge in the mouth, requiring surgical intervention.
Treatments for Alveolar Bone Loss
Bone Grafting: Used to restore lost bone in the alveolar process of maxilla bone and mandibular alveolar process.
Dental Implants: Help maintain bone structure by replacing lost teeth.
Orthodontic Treatment: Aligns teeth properly to distribute forces evenly across the alveolar ridge in the mouth.
The alveolar bone plays a vital role in dental health by supporting teeth within the dental alveoli.
Understanding its structure and function can help in preventing bone loss and maintaining oral health.
Proper dental care, including regular checkups and timely interventions, can preserve the alveolar process and ensure long-term dental stability (Lindhe, Lang, & Karring, 2008).
References:
Schroeder, H. E. (1986). Oral Structural Biology. Stuttgart: Thieme. Available at: https://www.thieme.com
Lindhe, J., Lang, N. P., & Karring, T. (2008). Clinical Periodontology and Implant Dentistry. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. Available at: https://www.wiley.com/en-us
Misch, C. E. (2007). Contemporary Implant Dentistry. St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier. Available at: https://www.elsevier.com
Ten Cate, A. R. (2012). Oral Histology: Development, Structure, and Function. St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier. Available at: https://www.elsevier.com
Contact Smiles
drdeepi15@gmail.com
Dr. Deepika B.D.S
© 2025 SmileWide Dental. All Rights Reserved.
Have doubts ..?


